Executive Summary
Prepared by Bhoir Exim Group – Active Exporter from India
India has emerged as a leading player in global fruit exports. In fiscal year 2024-25, India’s fruit and vegetable exports reached $3.87 billion, reflecting a growth rate of 5.67% compared to the previous year [1]. Over the past five years, exports have grown by 47.5%, and Indian fruits now reach 123 countries worldwide.
Based on Practical Export Experience and Current Market Data
This comprehensive guide provides all the necessary legal, technical, and practical information required for new and existing exporters to successfully export fruits from India. Drawing from years of hands-on experience in the fruit export industry, this guide covers market dynamics, regulatory compliance, cost management, and strategic market opportunities.
I. Fruit Export Guide: Market Analysis and Opportunities
Indian Fruit Production and Export (2024-25)
India is projected to produce a total of 1,145.10 million tons of fruits in 2024-25[4]. This includes bananas (380.35 million tons), mangoes (228.37 million tons), and other fruits. India produces 45.14% of the world’s mangoes and 43.26% of the world’s papayas, making it the largest producer of these fruits globally.
Top Export Markets
Indian fruits and vegetables are exported to 123 countries worldwide. The primary importing nations include:
- United Arab Emirates (Top destination for fresh produce)
- Nepal (Primary market for bananas)
- Netherlands (For processed foods)
- Malaysia, Sri Lanka, United Kingdom, Oman, and Qatar
- United States, China, and Saudi Arabia (For processed products)
In the past three years, 17 new markets have been added, including Brazil, Georgia, Uganda, Papua New Guinea, and Czech Republic.
GI-Tagged Fruits
Geographical Indication (GI) tagging plays a crucial role in enhancing the credibility and market value of Indian fruits. GI-tagged fruits such as Purander figs from Maharashtra have successfully entered premium markets like the United States, Middle East, and Hong Kong, commanding significantly higher prices than non-certified fruits.
II. Legal and Regulatory Requirements
1. IEC Code (Import-Export Code)
Requirement: It is mandatory for any business entity to obtain an IEC code before exporting fruits from India.
Issuing Authority: Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), Ministry of Commerce
Key Features:
- 10-digit alphanumeric code
- Application must be submitted with digital signature
- Mandatory documents: PAN certificate, company registration, identity proof
- Typically approved within 1-2 weeks
- Valid indefinitely for all transactions
2. APEDA Registration (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority)
Requirement: APEDA registration is mandatory for exporting fresh fruits and vegetables. APEDA is a government organization established under the 1985 Act that promotes and regulates the export of agricultural products.
Registration Process:
| Step | Description | Timeline |
| Step 1: IEC Acquisition | Obtain Import-Export Code from DGFT | 1-2 weeks |
| Step 2: Online Application | Register on APEDA website (apeda.gov.in) | 1-2 days |
| Step 3: Document Submission | Upload all required documents | 2-3 days |
| Step 4: Fee Payment | Pay ₹9,400 registration fee | Immediate |
| Step 5: Verification | APEDA conducts document verification | 5-7 days |
| Step 6: RCMC Issuance | Registration-cum-Membership Certificate issued | Immediate |
Table 1: APEDA Registration Timeline and Process Steps
APEDA Registration Fees:
- Government fee: ₹5,900 (including 18% GST)
- Professional fee: ₹3,500
- Total: ₹9,400
RCMC Validity: 5 years from the date of issue (automatic renewal possible)
Required Documents:
- Digital signature certificate
- Copy of PAN card
- Bank certificate (solvency certificate)
- Cancelled cheque from business account
- IEC code copy
- Company registration certificate (or partnership deed for partnerships)
- Proof of business address (electricity bill or rent agreement)
- Copy of FSSAI license
- List of directors/partners with their signatures
- Power of attorney (if applying through authorized representative)
3. FSSAI License (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India)
Requirement: FSSAI license is mandatory for all food exporters to ensure compliance with food safety standards.
License Types:
- Basic Registration: Annual turnover < ₹12 lakh
- FSSAI License: Annual turnover ₹12 lakh to ₹20 crore
- FSSAI License (Large Operations): Turnover > ₹20 crore
Required Documents:
- Business premises documents (rental agreement or ownership proof)
- Owner’s identity proof (Aadhar or passport)
- Certificate of incorporation
- Detailed bank account information
- APEDA registration certificate
4. Phytosanitary Certificate
Requirement: A phytosanitary certificate is essential for exporting fresh fruits and plant-based products.
Purpose: This certificate certifies that the product is free from harmful pests and diseases and complies with the plant health regulations of the importing country.
Issuing Authority: National Plant Protection Organization (NPPO) – Department of Ministry of Agriculture
Process:
- Collect all required documents (Forms 1 and 2, commercial invoice, packing list, export license)
- Arrange for mandatory plant inspection by authorized inspectors
- Conduct required phytosanitary treatments (fumigation, heat treatment, etc.) if necessary
- Submit application and documents to NPPO
- Certificate issued upon approval within 1-3 days
III. APEDA Support Schemes for Exporters
APEDA provides comprehensive financial assistance to fruit exporters in three main areas [5]:
1. Infrastructure Development Scheme
This scheme provides financial support for establishing and upgrading export infrastructure:
- Packhouses and modern grading lines
- Pre-cooling units for temperature regulation
- Cold storage facilities (both conventional and controlled atmosphere)
- Refrigerated transport vehicles (refer vans)
- Pre-shipment treatment facilities (irradiation, vapor heat, hot water dip systems)
- Laboratory testing equipment
- ERP systems for inventory management
2. Quality Development Scheme
This scheme focuses on improving product quality and compliance:
- Laboratory testing equipment and instruments
- Quality Management Systems (QMS) implementation
- Farm-level coordination and traceability systems
- Pesticide residue testing and monitoring
- ISO certification support
- Training programs for quality assurance personnel
3. Market Promotion Scheme
This scheme facilitates market access and brand building:
- Participation in international trade fairs and exhibitions
- Buyer-seller meets and networking events
- Packaging standards development and optimization
- Brand promotion and marketing activities
- Market research and intelligence gathering
Need Expert Guidance on APEDA Schemes?
Bhoir Exim Group assists exporters in accessing these schemes and optimizing benefits. Contact Us for Support
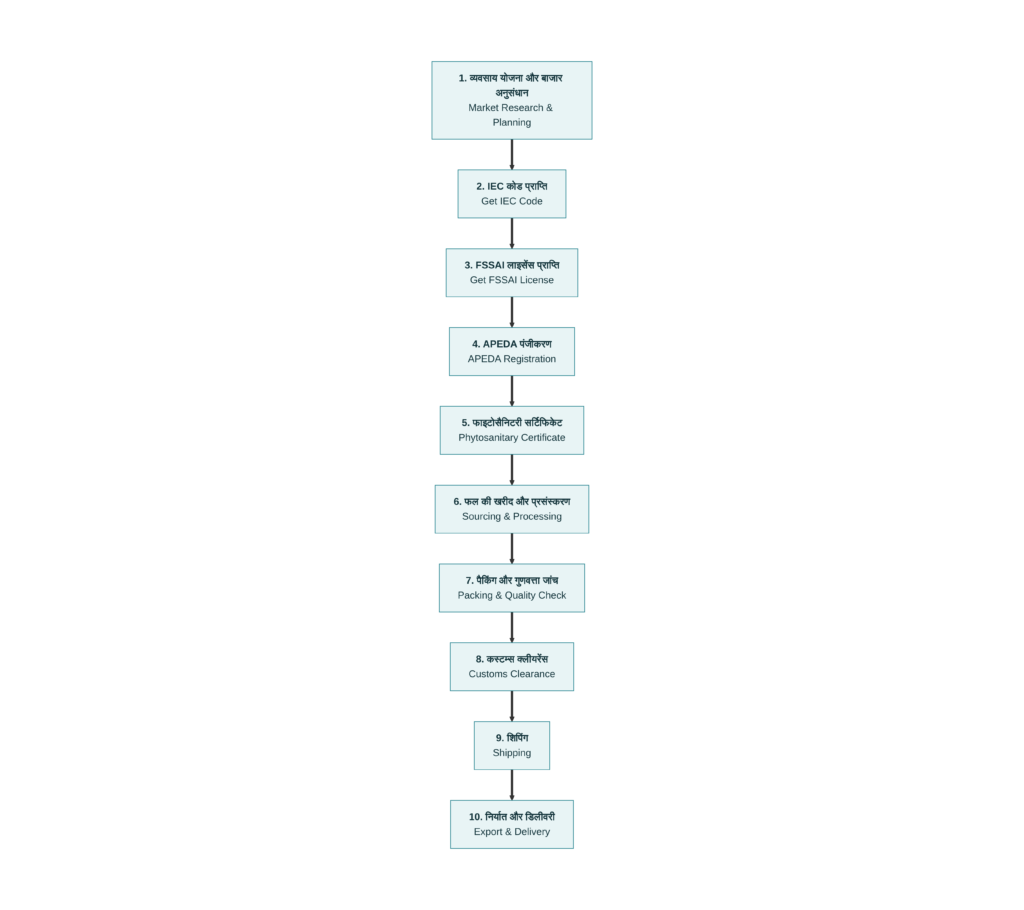
IV. Export Process: Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide
A. Initial Preparation and Planning
Step 1: Conduct Thorough Market Research
- Identify target countries based on demand and regulations
- Study imports regulations and tariff structures
- Analyze competitors and their market positioning
- Develop competitive pricing strategy
- Assess logistics and transportation feasibility
Step 2: Prepare Detailed Business Plan
- Define export business model and target segments
- Prepare financial projections and cash flow analysis
- Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies
- Plan for quality control and compliance
- Establish supply chain arrangements
B. Legal Compliance and Registration (2-4 weeks)
Sequential Registration Steps:
- Week 1-2: IEC Code Application and Approval
- Week 2-3: APEDA Online Registration and Document Upload
- Week 2-4: FSSAI License Processing
- Week 3-4: Phytosanitary Certificate Arrangement
- End of Week 4: All Certifications Ready for First Export
C. Fruit Sourcing and Quality Control
Export-Grade Quality Standards:
- Uniformity in color, size, and shape according to market requirements
- No major defects such as bruises, splits, spots, or rotting
- Appropriate ripeness level (varies by destination country)
- Pesticide residues within permissible international limits
- Microbiological safety and absence of pathogens
- Proper maturity index for extended shelf life
Sourcing Options:
- Direct purchase from own orchards (highest quality control)
- Agricultural cooperative societies (reliable supply)
- Wholesale agricultural markets (APMC) – largest selection
- Contract farming with individual farmers
D. Packing and Preparation
Packing Specifications:
- Use only food-grade materials certified for direct food contact
- Ensure proper ventilation to prevent moisture accumulation and spoilage
- Maintain consistent weight and dimensions for standardization
- Include comprehensive labeling with origin, grade, date, and barcodes
- Prepare packaging for temperature-controlled transportation
Packing Methods:
- Cardboard boxes (most common and economical)
- Plastic crates (reusable and environmentally friendly)
- EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) insulation layers
- Modified atmosphere packaging (for selected fruits with longer shelf life)
- Absorbent pads for moisture management
E. Export Documentation
Mandatory Documents for Export:
- Commercial Invoice
- Complete seller and buyer information
- Detailed product description, quantity, and unit price
- Total invoice value and payment terms
- Shipping address and delivery instructions
- Incoterms designation (FOB, CIF, etc.)
- Packing List
- Exact number of containers or packages
- Container marks and reference numbers
- Detailed contents of each package
- Weight and dimensions of each container
- Bill of Lading (B/L)
- Mandatory for sea freight shipments
- Complete details of shipper, carrier, and consignee
- Detailed description of goods
- Port of loading and discharge
- Estimated shipping timeline
- Phytosanitary Certificate
- Issued by NPPO confirming plant health
- Required for import into most countries
- Typically, valid for 14 days
- Certificate of Origin
- Confirms Indian origin of the produce
- Required for preferential tariff treatment
- APEDA Certificate
- Copy of RCMC when required by importing country
F. Customs Clearance Process
Indian Export Customs Procedure:
- File shipping bill with digital signature on Customs portal
- Pay all applicable export duties and fees
- Prepare shipping documentation and manifest
- Undergo physical inspection if randomly selected
- Obtain customs clearance permit
- File final manifest with customs authority
G. Shipping and Transportation
Shipping Options Comparison:
| Option | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Fruits | Cost/Unit |
| Sea Freight | Most economical for large quantities | Longer transit (2-4 weeks) | Bananas, mangoes, coconuts | ₹5-8/kg |
| Air Freight | Fastest delivery, fresher produce | Higher cost | Cherries, grapes, lychees | ₹25-40/kg |
| Road Transport | Flexible scheduling, regional | Limited distance (2-3 days) | Nearby Asia markets | ₹8-15/kg |
| Rail Transport | Cost-effective, reliable | Limited routes available | Heavy fruits (bulk) | ₹6-10/kg |
Table 2: Shipping Options Comparison and Cost Analysis
Recommended Logistics Partners:
- Cold-chain service providers with refrigerated facilities
- Freight forwarders specializing in perishables
- Customs clearing agents for smooth documentation
- Insurance providers for cargo protection
H. Delivery and Final Handover at Importing Country
- Quality inspection upon arrival at destination
- Submission of original documents with invoice
- Payment receipt confirmation from buyer
- Delivery confirmation and storage handover
V. Comprehensive Export-Related Cost Analysis
Exporters must carefully estimate the following major cost components:
| Cost Component | Estimated Range | Remarks |
| Agricultural Inputs | 30-50% | Fruit purchase, harvesting, initial transport |
| Packing Materials | 5-10% | Boxes, covers, labels, insulation materials |
| Processing and Grading | 3-8% | Cleaning, sorting, standardization |
| Testing and Certification | 2-5% | FSSAI, phytosanitary, quality testing |
| Cold Storage and Transport | 10-15% | Pre-cooling, cold storage, refrigerated shipping |
| Export Documentation | 1-3% | Shipping bill, B/L, commercial invoices |
| Customs and Insurance | 2-5% | Export duty, cargo insurance premium |
| Commission and Profit Margin | 15-25% | Middlemen commission, exporter profit |
Table 3: Comprehensive Export Cost Breakdown
Total Export Cost Estimate: ₹40-50 per kilogram (varies significantly based on fruit type, quality grade, and destination market)
For cost optimization strategies and customized export logistics planning, Contact Bhoir Exim Group
VI. Digital Trading and E-Commerce Opportunities
In 2025, there is significant expansion in fruit exports through digital platforms [9]:
- B2B Platforms: Alibaba, Global Sources, Trade Key for direct buyer connections
- Direct E-Commerce: Amazon International, Shopify for retail consumers
- Agricultural Data: APEDA’s data portal providing real-time market information
- Digital Payments: Escrow services and blockchain for transaction security
- Supply Chain Digitization: IoT sensors for real-time shipment tracking
VII. Opportunities and Challenges in 2025
Positive Opportunities for Growth
- Strong Export Growth Trajectory: 47.5% cumulative growth over past 5 years indicates sustained demand [2]
- Access to Emerging Markets: Entry into 17 new countries in recent years [3]
- Government Support Infrastructure: Comprehensive APEDA assistance schemes and incentives [5]
- GI-Tagging Premium Pricing: GI-tagged fruits command 30-50% price premium [6]
- Improving Cold-Chain Infrastructure: Government investment in refrigeration facilities
- Quality Standardization: Increasing compliance with international standards
- Rising Global Demand: Growing middle class in Asia seeking premium fruits
Key Challenges to Address
- Competitive Global Market: Strong competition from Egypt, Spain, Turkey, and other exporters
- High Logistics Costs: Transportation expenses significantly impact profit margins
- Insufficient Cold-Chain Infrastructure: Inadequate refrigerated storage in some regions
- Stringent Quality Standards: Meeting multiple international certifications and standards
- Market Access Barriers: Tariffs and non-tariff barriers in developed countries
- Climate Volatility: Unpredictable weather affecting production and export timing
- Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate variations affecting competitiveness
VIII. Best Practices for Successful Fruit Exporters
- Prioritize Premium Quality: Superior quality is essential for achieving better prices and market reputation
- Strategic Market Selection: Begin with neighboring Asian markets before attempting developed countries
- Long-Term Buyer Relationships: Establish stable, multi-year supply agreements with key buyers
- Supply Chain Transparency: Implement complete traceability throughout the supply chain
- Strategic Branding: Pursue GI-tagging and develop strong brand identity for premium positioning
- Product Diversification: Diversify fruit offerings rather than depending on single product
- Digital Integration: Leverage trading platforms, data analytics, and IoT for efficiency
IX. Major Exportable Fruits and Market Opportunities
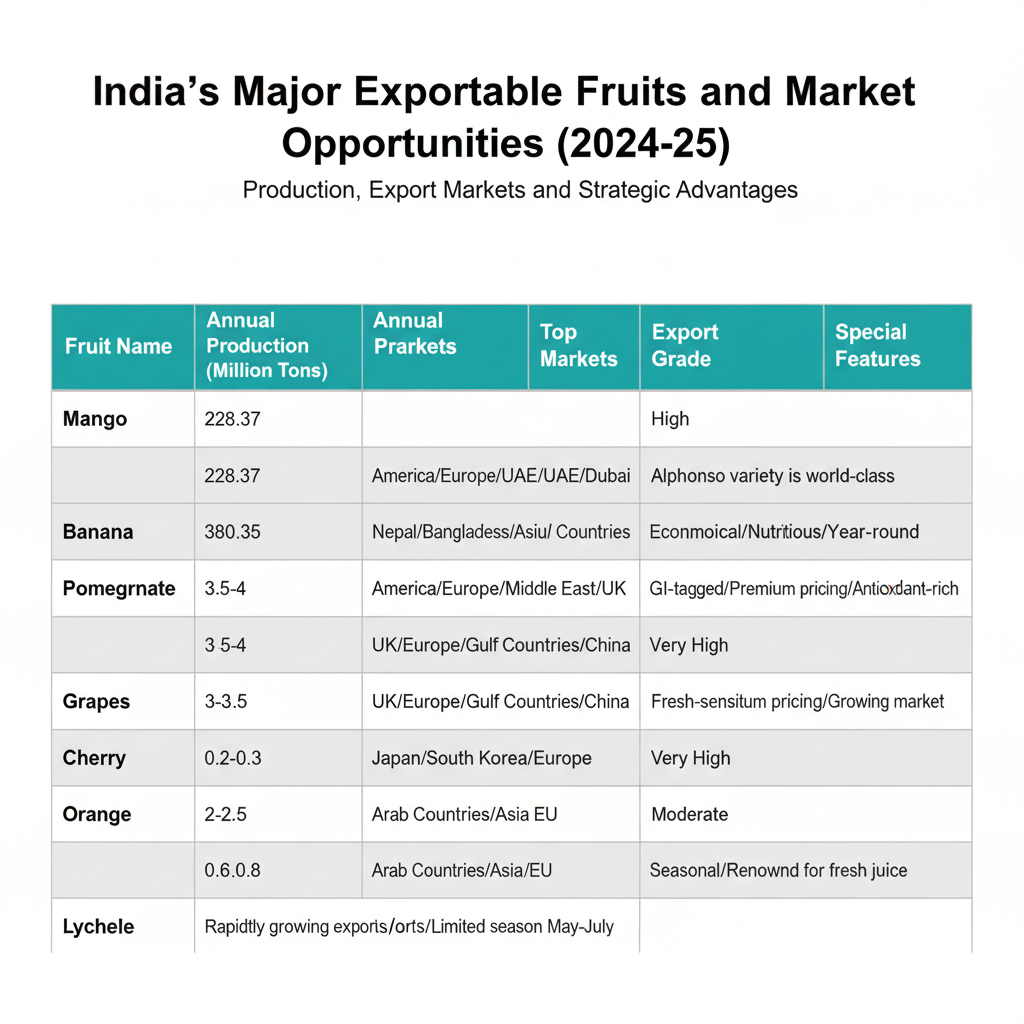
Mango (Mangifera indica)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 228.37 million tons
- Global Market Share: 45.14% (world’s largest producer)
- Primary Export Markets: USA, Europe, UAE, Dubai, United Kingdom
- Export Grade Potential: Premium quality
- Unique Characteristics: Alphonso variety commands premium prices internationally; known as “king of fruits”
- Shelf Life: 7-14 days at room temperature; 3-4 weeks in cold storage
- Peak Export Season: April-July
- Key Export Regions: Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh
Mango Export Strategy: Focus on Alphonso variety for premium markets, develop direct relationships with European and American retailers, implement proper ripening protocols.
Banana (Musa paradisiaca)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 380.35 million tons (highest among all fruits in India)
- Primary Export Markets: Nepal, Bangladesh, throughout Southeast Asia, Gulf countries
- Export Grade Potential: High volume, consistent quality
- Unique Characteristics: Economical, highly nutritious, available year-round
- Shelf Life: 5-10 days at room temperature; 2-3 weeks in cold storage
- Peak Export Season: Year-round availability with seasonal peaks
- Key Export Regions: Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka
Banana Export Opportunity: Establish bulk contracts with South Asian distributors, focus on consistency and volume, develop organic banana certifications for premium pricing.
Pomegranate (Punica granatum)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 3.5-4 million tons
- Primary Export Markets: USA, European Union, Middle East, United Kingdom
- Export Grade Potential: Very high quality and pricing
- Unique Characteristics: GI-tagged varieties available; premium pricing; rich in antioxidants
- Shelf Life: 30-40 days in cold storage; longer under CA (Controlled Atmosphere)
- Peak Export Season: September-October
- Key Export Regions: Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat, Rajasthan
- Market Premium: GI-tagged pomegranates fetch 30-50% higher prices
Pomegranate Export Strategy: Pursue GI-tagging certification, target premium American and European health-conscious consumers, develop branded packaging.
Grapes (Vitis vinifera)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 3-3.5 million tons
- Primary Export Markets: United Kingdom, Continental Europe, Gulf states, China
- Export Grade Potential: High quality and volume
- Unique Characteristics: Fresh-sensitive requiring careful handling; excellent shelf life
- Shelf Life: 3-4 weeks with proper storage and atmosphere control
- Peak Export Season: May-September
- Key Export Regions: Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh
- Special Note: Seedless varieties particularly valued in international markets
Grape Export Opportunity: Specialize in seedless varieties, invest in controlled atmosphere storage, build relationships with UK and European retailers.
Cherries (Prunus avium)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 0.2-0.3 million tons
- Primary Export Markets: Japan, South Korea, Europe, Middle East
- Export Grade Potential: Very high (premium segment)
- Unique Characteristics: Rare fruit with strong demand in Asian markets; commands premium pricing
- Shelf Life: 10-14 days in cold storage under optimal conditions
- Peak Export Season: March-May
- Key Export Regions: Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand
- Market Potential: Rapidly growing market with shortage of supply
Cherry Export Strategy: Target luxury Asian markets (Japan, South Korea), develop premium packaging, create supply relationships with distributors early in season.
Oranges (Citrus sinensis)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 2-2.5 million tons
- Primary Export Markets: Arab countries, Southeast Asia, European Union
- Export Grade Potential: Moderate to high
- Unique Characteristics: Seasonal availability; renowned for fresh juice production
- Shelf Life: 4-8 weeks in cold storage
- Peak Export Season: October-March
- Key Export Regions: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh
- Value Addition: Fresh juice concentrates increasingly popular in exports
Orange Export Opportunity: Develop juice concentrate value-added products, establish contracts with juice manufacturers, focus on Arab and Asian markets.
Lychee (Litchi chinensis)
- Annual Production (2024-25): 0.6-0.8 million tons
- Primary Export Markets: Asia (primary), China, Hong Kong, Singapore, Thailand
- Export Grade Potential: High (specialty product)
- Unique Characteristics: Rapidly growing export market; limited seasonal availability creates scarcity value
- Shelf Life: 2-3 weeks in cold storage; requires careful temperature management
- Peak Export Season: May-July (very limited window)
- Key Export Regions: Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Assam
- Market Dynamics: Strong demand from Chinese diaspora globally
Lychee Export Strategy: Pre-arrange buyers before harvest season, maintain strict cold-chain logistics, target premium Asian consumers seeking fresh lychees.
X. Key Success Factors for 2025 and Beyond
Strategic Planning Elements
- Market Intelligence: Stay updated with import regulations, tariffs, and market trends
- Quality Assurance: Implement certified quality management systems
- Cost Management: Continuously optimize supply chain to maintain competitiveness
- Risk Management: Develop contingency plans for climate, market, and logistical disruptions
- Technology Adoption: Use digital tools for traceability, tracking, and market access
- Compliance Excellence: Maintain highest standards for all certifications and regulations
Competitive Differentiation
- Develop unique value propositions (organic, fair trade, heritage varieties)
- Build direct relationships with premium retailers and distributors
- Invest in sustainable agriculture and environmental practices
- Create appealing packaging and branding for consumer appeal
- Establish long-term contracts with reliable buyers
Bhoir Exim Group: Your Export Partner
For export inquiries, sourcing, documentation support, or market guidance:
Services Offered:
- Sourcing and quality assurance
- APEDA and regulatory compliance support
- Export documentation and logistics coordination
- Market identification and buyer connections
- Cold-chain management and transportation
- Consulting on cost optimization and market strategy
Appendix: Quick Reference Guide
Important Government Agencies
- APEDA: www.apeda.gov.in
- DGFT: www.dgft.gov.in
- FSSAI: www.fssai.gov.in
- Ministry of Agriculture: www.agriculture.gov.in
- State Agriculture Departments: Respective state portals
Export Promotion Organizations
- Federation of Indian Export Organizations (FIEO)
- Agricultural Exports Promotion Council
- Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority
References
[1] APEDA Export Statistics, 2024-25 (Fruit and Vegetable Exports Report)
[2] Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Annual Report 2024-25
[3] APEDA Official Announcements, New Market Entries 2022-25
[4] Agricultural Statistics at a Glance, 2024
[5] APEDA Support Schemes and Financial Assistance Programs
[6] Geographical Indication Registry Database and GI Premium Research
[7] APEDA and FSSAI Official Guidelines and Procedures
[8] NPPO Phytosanitary Certificate Requirements and Standards
[9] Digital Agriculture Platform Analysis, Indian Export-Import Statistics 2025
Document Version: 1.2 (Updated December 2025)
Last Modified: December 27, 2025
Prepared by: Bhoir Exim Group
Applicable: India Fruit Export Regulations 2024-25
This guide is intended for informational purposes and reflects current regulations and market conditions as of December 2025. Exporters are advised to verify all regulatory requirements with official authorities before commencing operations.
Fresh Produce From Indian Farms to Global Markets